Create a React dapp with local state
This tutorial walks you through integrating a simple React dapp with MetaMask. The dapp has a single component, so only requires managing local state. You'll use the Vite build tool with React and TypeScript to create the dapp.
This tutorial builds up your knowledge of working with MetaMask incrementally; this means you won't implement the best solution at first, but you'll experiment with the MetaMask API and continually work towards better solutions.
React is familiar to most web developers, and it makes it easy to work with state management and build with components that need updating.
You can see the source code for the starting point and final state of this dapp.
Prerequisites
- Node.js version 18+
- npm version 9+
- A text editor (for example, VS Code)
- The MetaMask extension installed
- Basic knowledge of JavaScript and React
Steps
1. Set up the project
Set up a new project using Vite, React, and TypeScript, by running the following command:
npm create vite@latest mm-dapp-react -- --template react-ts
Install the node module dependencies:
cd mm-dapp-react && npm install
Launch the development server:
npm run dev
This displays a localhost URL on your terminal. Copy this URL into your browser and open it.
You can use the npx vite or npm run dev command to run your project at any time if the
development server has been stopped.
Open the project in a text editor.
To start with a blank slate, replace the code in src/App.tsx with the following:
import './App.css'
const App = () => {
return (
<div className="App">
<button>Connect MetaMask</button>
</div>
)
}
export default App
You'll need to get around type-checking by defining the window.ethereum object as any.
Update src/vite-env.d.ts to the following:
/// <reference types="vite/client" />
interface Window {
ethereum: any;
}
Also, update src/App.css to the following:
.App {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
place-items: center;
min-width: 100vw;
min-height: 100vh;
}
button {
margin-top: 0.5em;
}
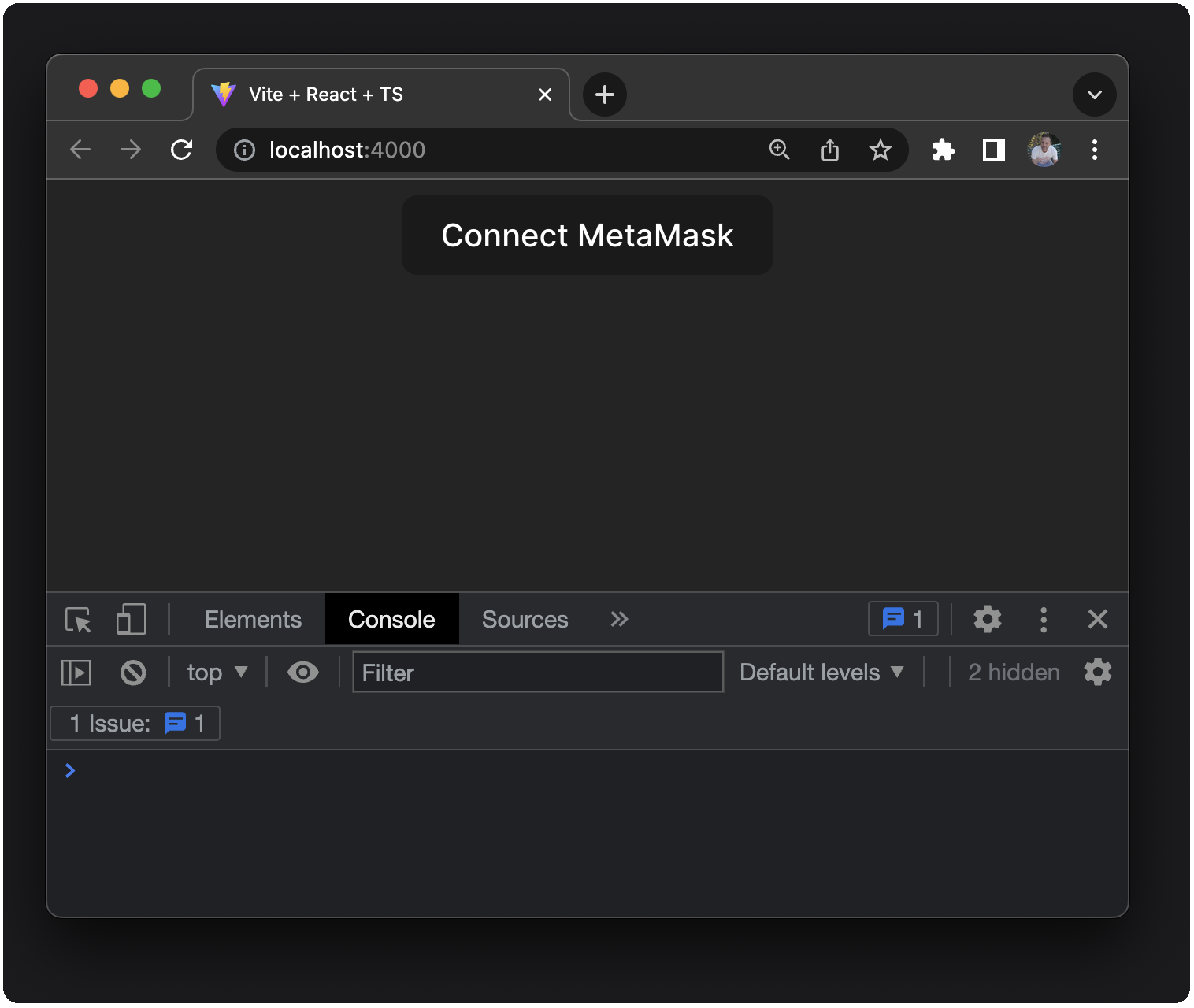
At this point, you have a working React app with some basic styling and a button that you'll use to connect to MetaMask.
2. Detect MetaMask
Next, detect the injected provider that browser extension wallets use. MetaMask injects a JavaScript Ethereum provider into the browser at window.ethereum. You will use this provider in your dapp to request user information from Metamask.
Add code to conditionally render a Connect MetaMask button in your component by updating
src/App.tsx to the following:
import './App.css'
let injectedProvider = false
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
injectedProvider = true
console.log(window.ethereum)
}
const isMetaMask = injectedProvider ? window.ethereum.isMetaMask : false
const App = () => {
return (
<div className="App">
<h2>Injected Provider { injectedProvider ? 'DOES' : 'DOES NOT'} Exist</h2>
{ isMetaMask &&
<button>Connect MetaMask</button>
}
</div>
)
}
export default App
If you don't have the MetaMask browser extension installed or enabled, you won't see a Connect MetaMask button, and the text displays Injected Provider DOES NOT Exist.
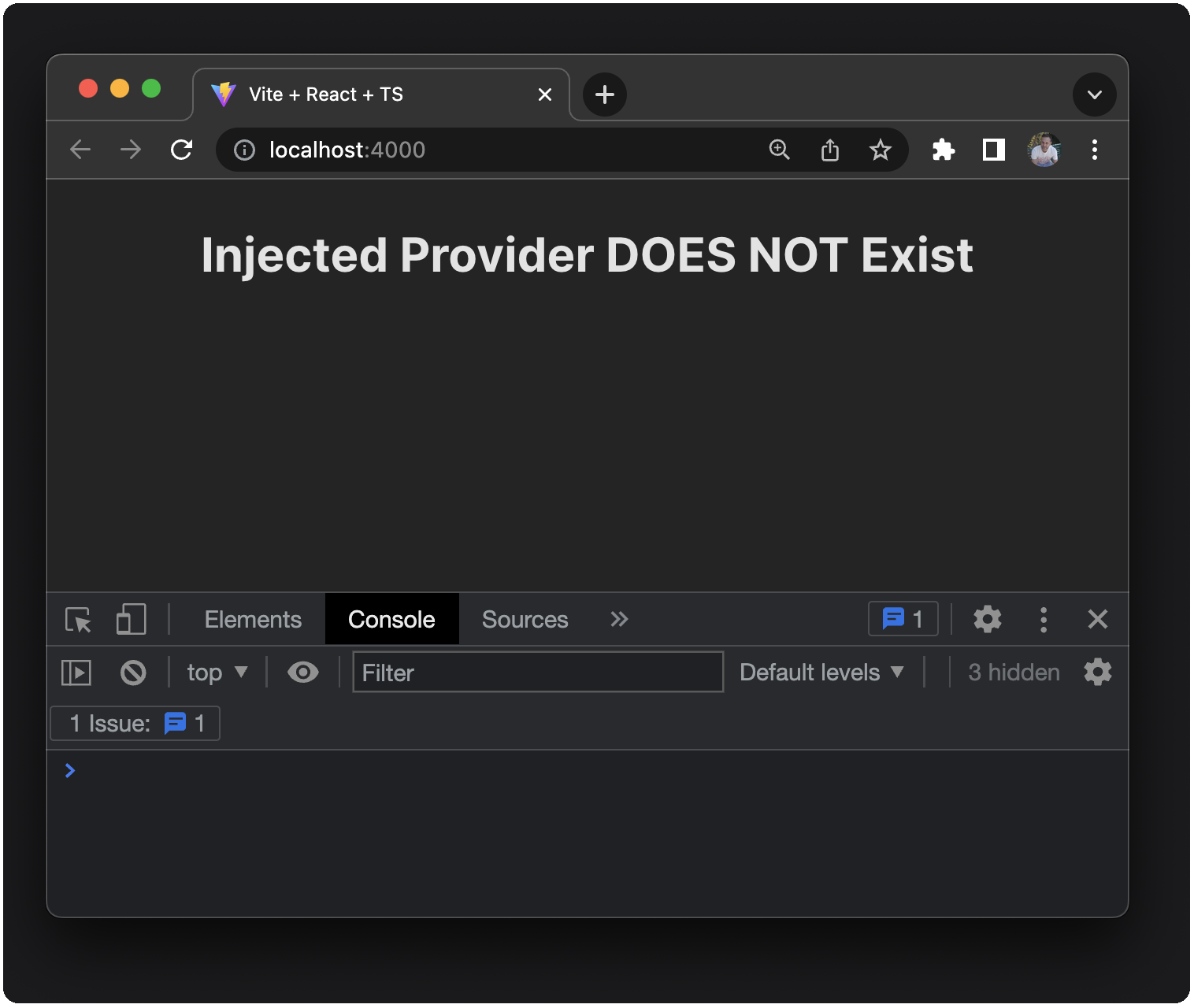
If you have the extension installed and enabled, you'll see the Connect MetaMask button and the text displays Injected Provider DOES Exist.
You'll also see the ethereum provider printed to the console.
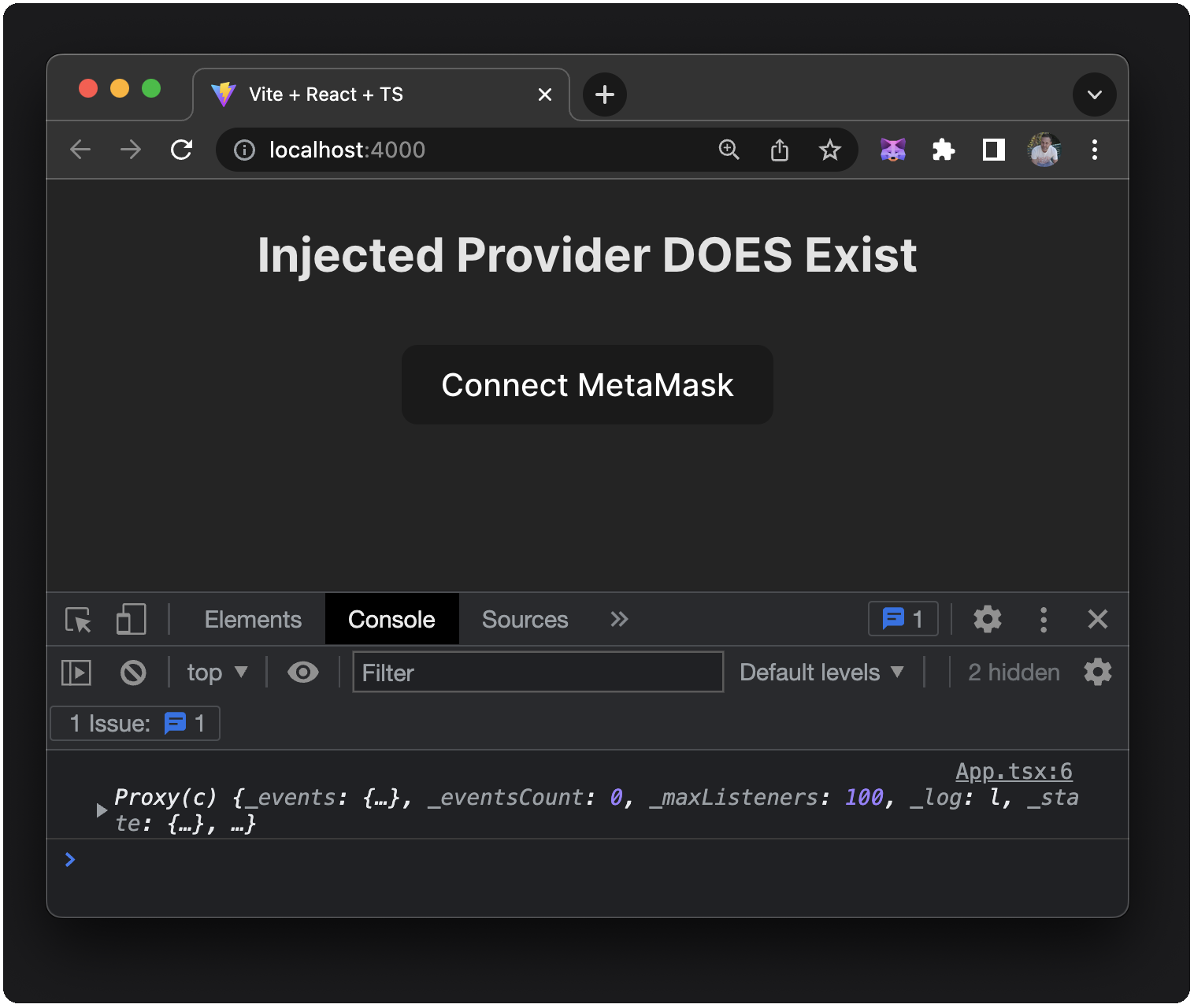
You can toggle back and forth between these two states by enabling and disabling the MetaMask extension from your browser's Manage Extensions menu.
Use @metamask/detect-provider
Developers often use the previous approach when tasked with detecting an injected provider (wallet extension).
However, MetaMask provides the
@metamask/detect-provider module to detect the
MetaMask Ethereum provider or any provider injected at window.ethereum on any platform or browser.
We recommend using @metamask/detect-provider
instead of manually detecting the provider yourself.
In your project directory (the mm-dapp-react directory), install the module using the following command:
npm install @metamask/detect-provider
Update src/App.tsx to the following:
import './App.css'
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import detectEthereumProvider from '@metamask/detect-provider'
const App = () => {
const [hasProvider, setHasProvider] = useState<boolean | null>(null)
useEffect(() => {
const getProvider = async () => {
const provider = await detectEthereumProvider({ silent: true })
console.log(provider)
setHasProvider(Boolean(provider)) // transform provider to true or false
}
getProvider()
}, [])
return (
<div className="App">
<div>Injected Provider {hasProvider ? 'DOES' : 'DOES NOT'} Exist</div>
{ hasProvider &&
<button>Connect MetaMask</button>
}
</div>
)
}
export default App
This code creates a piece of local state called hasProvider of type boolean or null value,
initialized with a null value.
Next, it creates a useEffect with zero dependencies (it only runs once in your component lifecycle).
React's useEffect hook allows components to run code when a component is mounted or when some
property's state changes.
This hook also allows cleaning up when the component is unmounted.
If you explicitly declare no dependencies by passing in an empty array, then useEffect only runs
once before the component mounts.
Inside useEffect, there's an async function called getProvider.
This function awaits the detectEthereumProvider and uses an option (silent: true) to silence any
console errors related to the provider not being available.
You can choose not to use that option if you prefer.
The setter function within useEffect transforms the provider's detection to a boolean value.
If you run the code now, you'll see the same result in your dapp, but you're using
@metamask/detect-provider instead of your own code.
3. Connect to MetaMask
To connect your dapp to MetaMask, you'll create another useState named wallet, which keeps your
dapp up to date with various MetaMask wallet properties such as accounts, balance, and chainId.
These are essential properties to sync with your dapp constantly.
You'll first add a state for accounts and slowly build up your state over the following few
tutorial sections.
You'll also set up a button to connect to the MetaMask wallet.
Update the src/App.tsx to the following:
import './App.css'
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import detectEthereumProvider from '@metamask/detect-provider'
const App = () => {
const [hasProvider, setHasProvider] = useState<boolean | null>(null)
const initialState = { accounts: [] } /* New */
const [wallet, setWallet] = useState(initialState) /* New */
useEffect(() => {
const getProvider = async () => {
const provider = await detectEthereumProvider({ silent: true })
setHasProvider(Boolean(provider))
}
getProvider()
}, [])
const updateWallet = async (accounts:any) => { /* New */
setWallet({ accounts }) /* New */
} /* New */
const handleConnect = async () => { /* New */
let accounts = await window.ethereum.request({ /* New */
method: "eth_requestAccounts", /* New */
}) /* New */
updateWallet(accounts) /* New */
} /* New */
return (
<div className="App">
<div>Injected Provider {hasProvider ? 'DOES' : 'DOES NOT'} Exist</div>
{ hasProvider && /* Updated */
<button onClick={handleConnect}>Connect MetaMask</button>
}
{ wallet.accounts.length > 0 && /* New */
<div>Wallet Accounts: { wallet.accounts[0] }</div>
}
</div>
)
}
export default App
The comments in the code snippet indicate any new or updated lines of code. The changes include:
Lines 7-8: Create an object representing the initial empty state and a new
useStatehook to reflect your MetaMask wallet state.Lines 19-21: Add an
updateWalletfunction that sets your new wallet state when you connect. This will also be called when you add code later that refreshes our wallet state. This function will be helpful as you start syncing thebalanceandchainId.Lines 23-28: Add a
handleConnectfunction that the UI calls to connect to MetaMask usingwindow.ethereum.requestand theeth_requestAccountsRPC method. Your dapp stores the result from this RPC call in a variable namedaccountsand passes it to theupdateWalletfunction.Lines 34-36: On click, the Connect MetaMask button calls
handleConnect, from which an RPC call ofeth_requestAccountsis awaited, and the user is prompted to connect to MetaMask: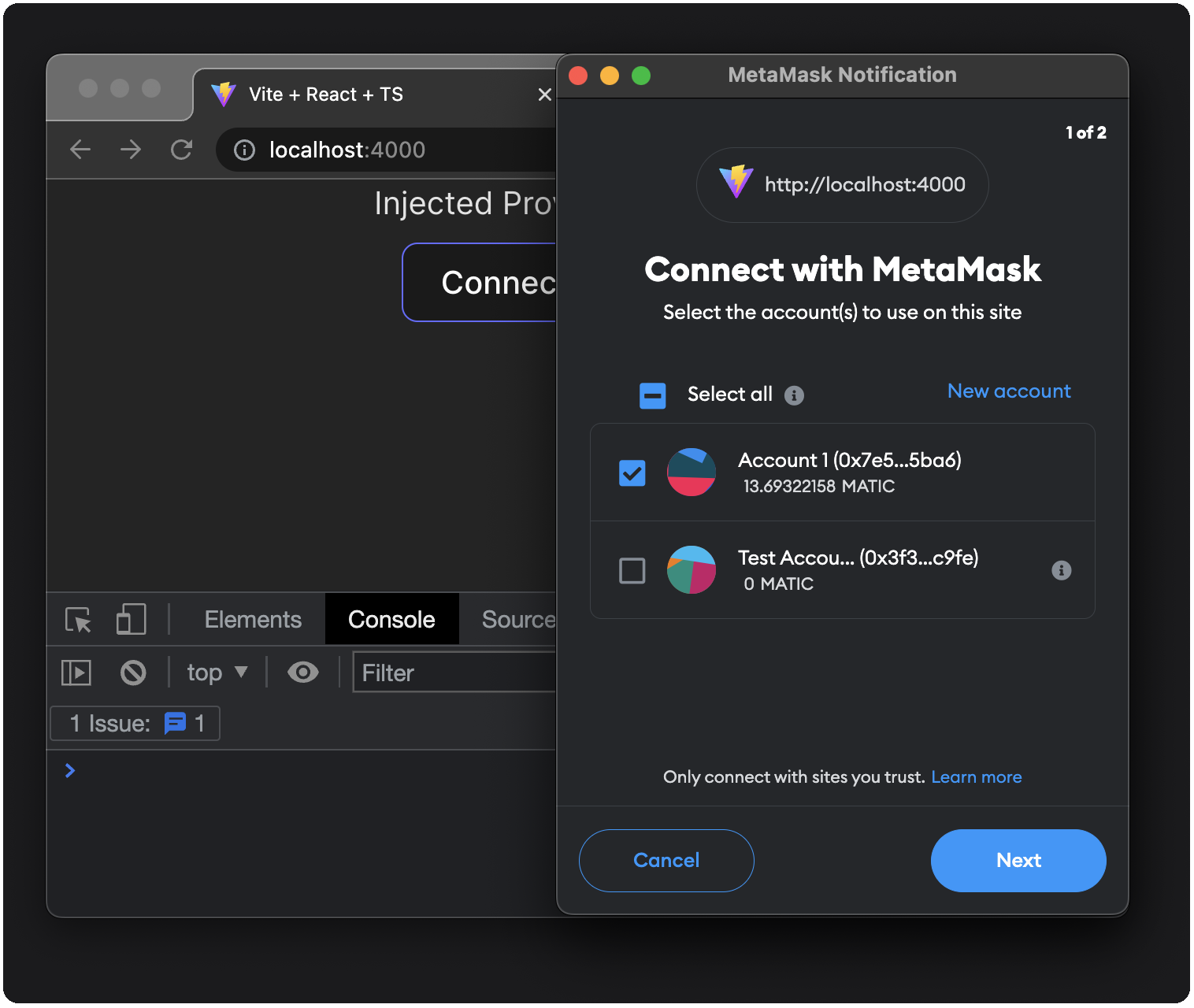
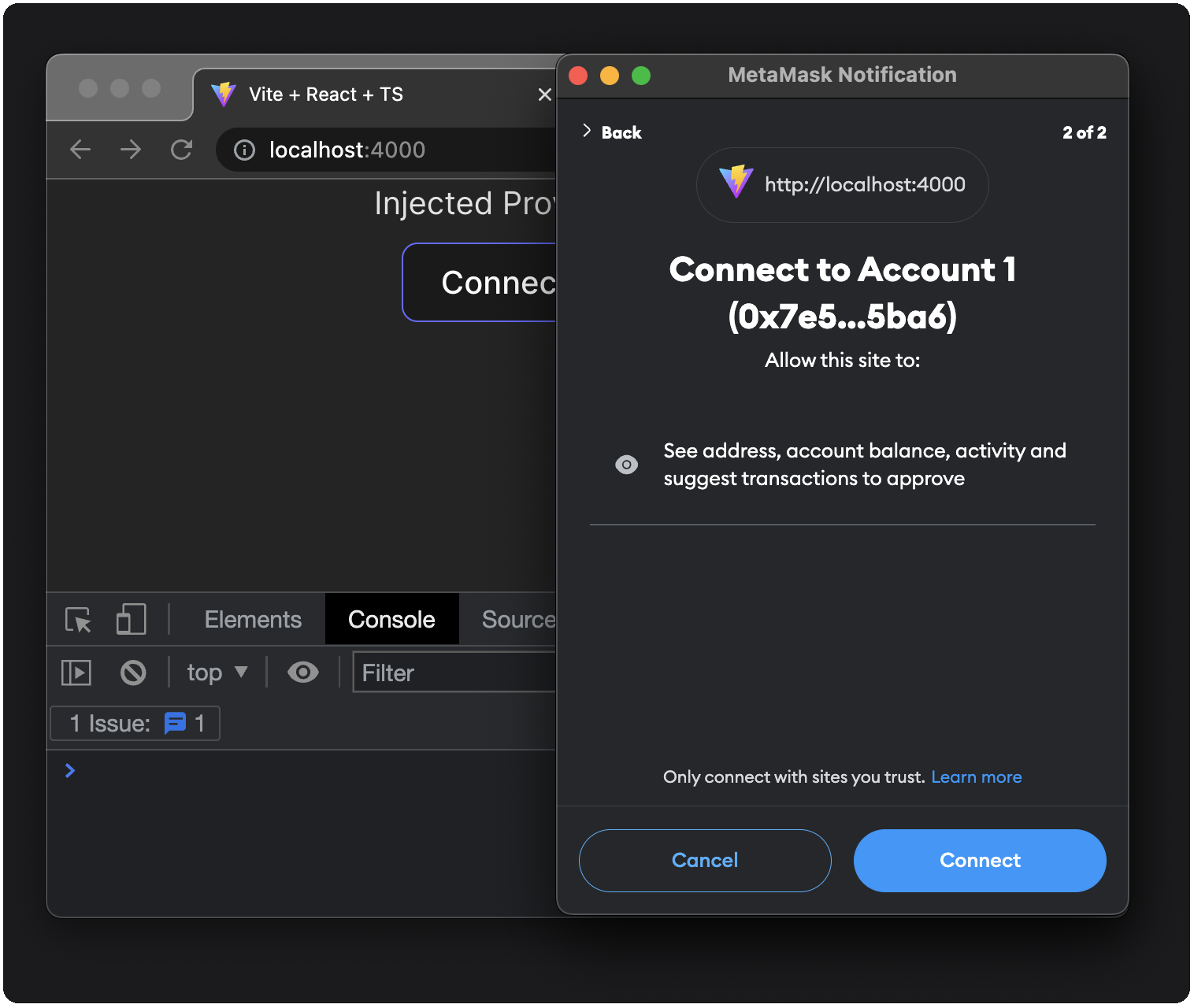
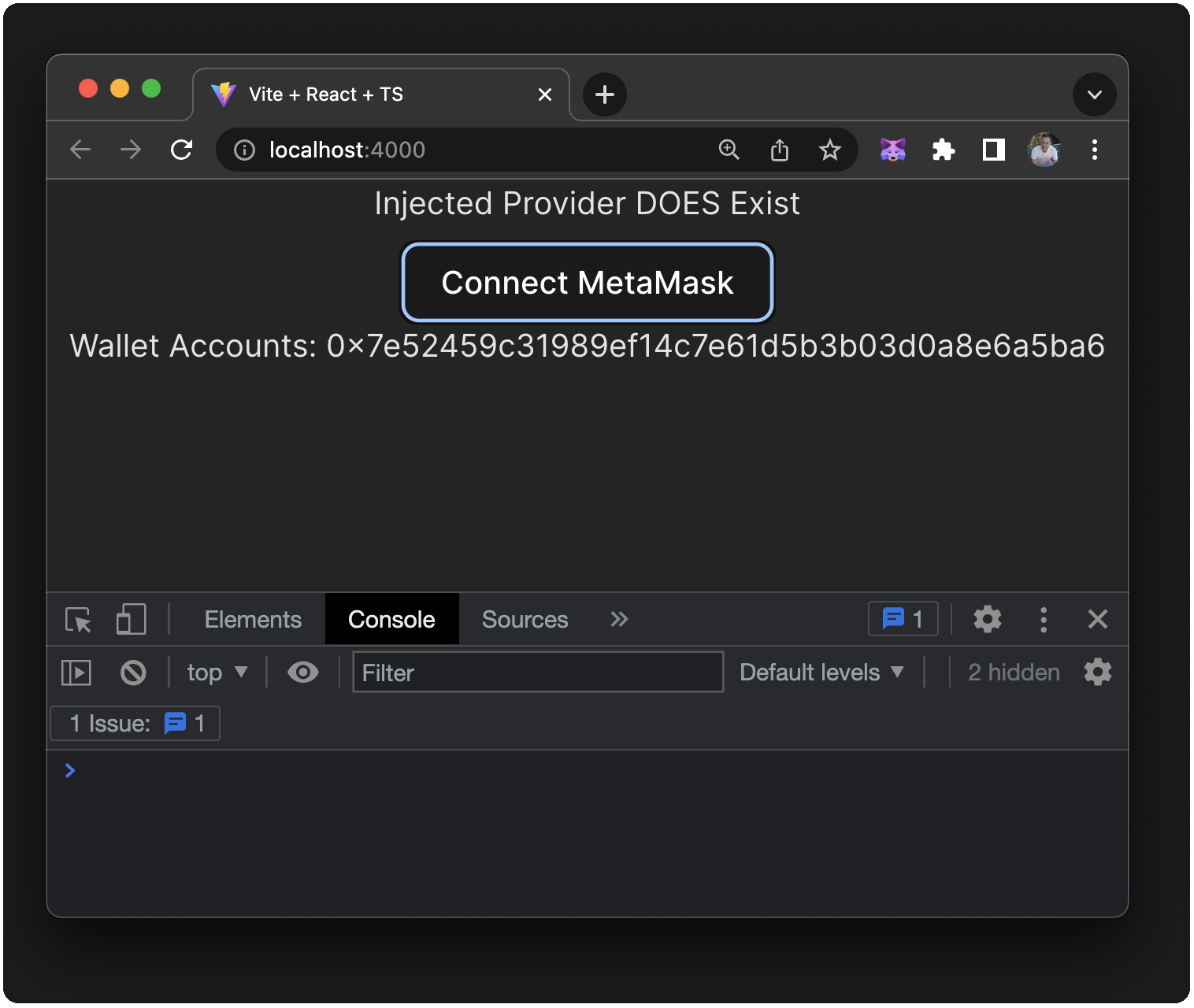
Lines 38-40: Once connected, you'll see your account address displayed in your dapp:
4. Handle state change
With the current code, your dapp loses the account data if you refresh the page.
When you connect using the button, the dapp sets accounts in its state, but in the case of a
browser refresh, you need something in useEffect to check if you've already connected and update
the wallet state.
Thinking ahead, once you track more than just accounts, you also need a mechanism to get the
balance and chainId and update their state.
Update src/App.tsx with some added logic to useEffect:
import './App.css'
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import detectEthereumProvider from '@metamask/detect-provider'
const App = () => {
const [hasProvider, setHasProvider] = useState<boolean | null>(null)
const initialState = { accounts: [] }
const [wallet, setWallet] = useState(initialState)
useEffect(() => {
const refreshAccounts = (accounts: any) => { /* New */
if (accounts.length > 0) { /* New */
updateWallet(accounts) /* New */
} else { /* New */
// if length 0, user is disconnected /* New */
setWallet(initialState) /* New */
} /* New */
} /* New */
const getProvider = async () => {
const provider = await detectEthereumProvider({ silent: true })
setHasProvider(Boolean(provider))
if (provider) { /* New */
const accounts = await window.ethereum.request( /* New */
{ method: 'eth_accounts' } /* New */
) /* New */
refreshAccounts(accounts) /* New */
window.ethereum.on('accountsChanged', refreshAccounts) /* New */
} /* New */
}
getProvider()
return () => { /* New */
window.ethereum?.removeListener('accountsChanged', refreshAccounts)
} /* New */
}, [])
const updateWallet = async (accounts:any) => {
setWallet({ accounts })
}
const handleConnect = async () => {
let accounts = await window.ethereum.request({
method: "eth_requestAccounts",
})
updateWallet(accounts)
}
return (
<div className="App">
<div>Injected Provider {hasProvider ? 'DOES' : 'DOES NOT'} Exist</div>
{ window.ethereum?.isMetaMask && wallet.accounts.length < 1 && /* Updated */
<button onClick={handleConnect}>Connect MetaMask</button>
}
{ wallet.accounts.length > 0 &&
<div>Wallet Accounts: { wallet.accounts[0] }</div>
}
</div>
)
}
export default App
Note that useEffect is a side effect; you use the hooks for fetching data, reading and writing to
local storage, and setting up event listeners or subscriptions.
The side effect occurs on the first render only since you have nothing in your dependency array. You also need to clean up those listeners upon unmount of your component.
You can now test your dapp and see that when you refresh the page, you retain the display of the user's address. You can also disable the Metamask browser extension, enable it again, and reconnect to it. You will see that the React dapp has retained the user address.
You've synced with a source outside your dapp and managed the state in a single component.
In learning how to connect to MetaMask from a React application, you've learned how to track some essential state of your wallet, precisely, which account is selected and active in the MetaMask wallet.
Your dapp syncs this state locally using React's useState and the React useEffect hooks.
The dapp ensures that if a user manually disconnects or changes the account, or refreshes the page,
the component is aware of any state change.
5. Manage more MetaMask state
Next, you'll add balance and chainId to your state.
Before editing src/App.tsx, you need a few utility functions to format balance and chainId.
Create a new file at src/utils/index.tsx with the following code:
export const formatBalance = (rawBalance: string) => {
const balance = (parseInt(rawBalance) / 1000000000000000000).toFixed(2)
return balance
}
export const formatChainAsNum = (chainIdHex: string) => {
const chainIdNum = parseInt(chainIdHex)
return chainIdNum
}
With those functions exported, you can import them into your component and use them to get human-readable balance and chain information.
Watch user balance and chain
To display the connected address's balance and the current chain ID, you need to update the
initialState object in your component.
Since your dapp already uses eth_requestAccounts to determine the accounts, you need to add a
dependent call to eth_getBalance once you have that account information.
Finally, you need to parse the returned value of the balance and format it into a human-readable string.
You'll also create a function called formatBalance.
Update src/App.tsx to the following:
import './App.css'
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import { formatBalance, formatChainAsNum } from './utils' /* New */
import detectEthereumProvider from '@metamask/detect-provider'
const App = () => {
const [hasProvider, setHasProvider] = useState<boolean | null>(null)
const initialState = { accounts: [], balance: "", chainId: "" } /* Updated */
const [wallet, setWallet] = useState(initialState)
useEffect(() => {
const refreshAccounts = (accounts: any) => {
if (accounts.length > 0) {
updateWallet(accounts)
} else {
// if length 0, user is disconnected
setWallet(initialState)
}
}
const refreshChain = (chainId: any) => { /* New */
setWallet((wallet) => ({ ...wallet, chainId })) /* New */
} /* New */
const getProvider = async () => {
const provider = await detectEthereumProvider({ silent: true })
setHasProvider(Boolean(provider))
if (provider) {
const accounts = await window.ethereum.request(
{ method: 'eth_accounts' }
)
refreshAccounts(accounts)
window.ethereum.on('accountsChanged', refreshAccounts)
window.ethereum.on("chainChanged", refreshChain) /* New */
}
}
getProvider()
return () => {
window.ethereum?.removeListener('accountsChanged', refreshAccounts)
window.ethereum?.removeListener("chainChanged", refreshChain) /* New */
}
}, [])
const updateWallet = async (accounts:any) => {
const balance = formatBalance(await window.ethereum!.request({ /* New */
method: "eth_getBalance", /* New */
params: [accounts[0], "latest"], /* New */
})) /* New */
const chainId = await window.ethereum!.request({ /* New */
method: "eth_chainId", /* New */
}) /* New */
setWallet({ accounts, balance, chainId }) /* Updated */
}
const handleConnect = async () => {
let accounts = await window.ethereum.request({
method: "eth_requestAccounts",
})
updateWallet(accounts)
}
return (
<div className="App">
<div>Injected Provider {hasProvider ? 'DOES' : 'DOES NOT'} Exist</div>
{ window.ethereum?.isMetaMask && wallet.accounts.length < 1 &&
<button onClick={handleConnect}>Connect MetaMask</button>
}
{ wallet.accounts.length > 0 &&
<> {/* New */}
<div>Wallet Accounts: {wallet.accounts[0]}</div>
<div>Wallet Balance: {wallet.balance}</div> {/* New */}
<div>Hex ChainId: {wallet.chainId}</div> {/* New */}
<div>Numeric ChainId: {formatChainAsNum(wallet.chainId)}</div> {/* New */}
</>
}
</div>
)
}
export default App
The changes here are minimal because you only need to update or duplicate existing functionality and add a few utility functions.
Your dapp now displays account, balance, and chainId. The chainId is represented in both hex and decimal formats. The values on your display reflect your MetaMask wallet contents and may not be the same as in the following example.
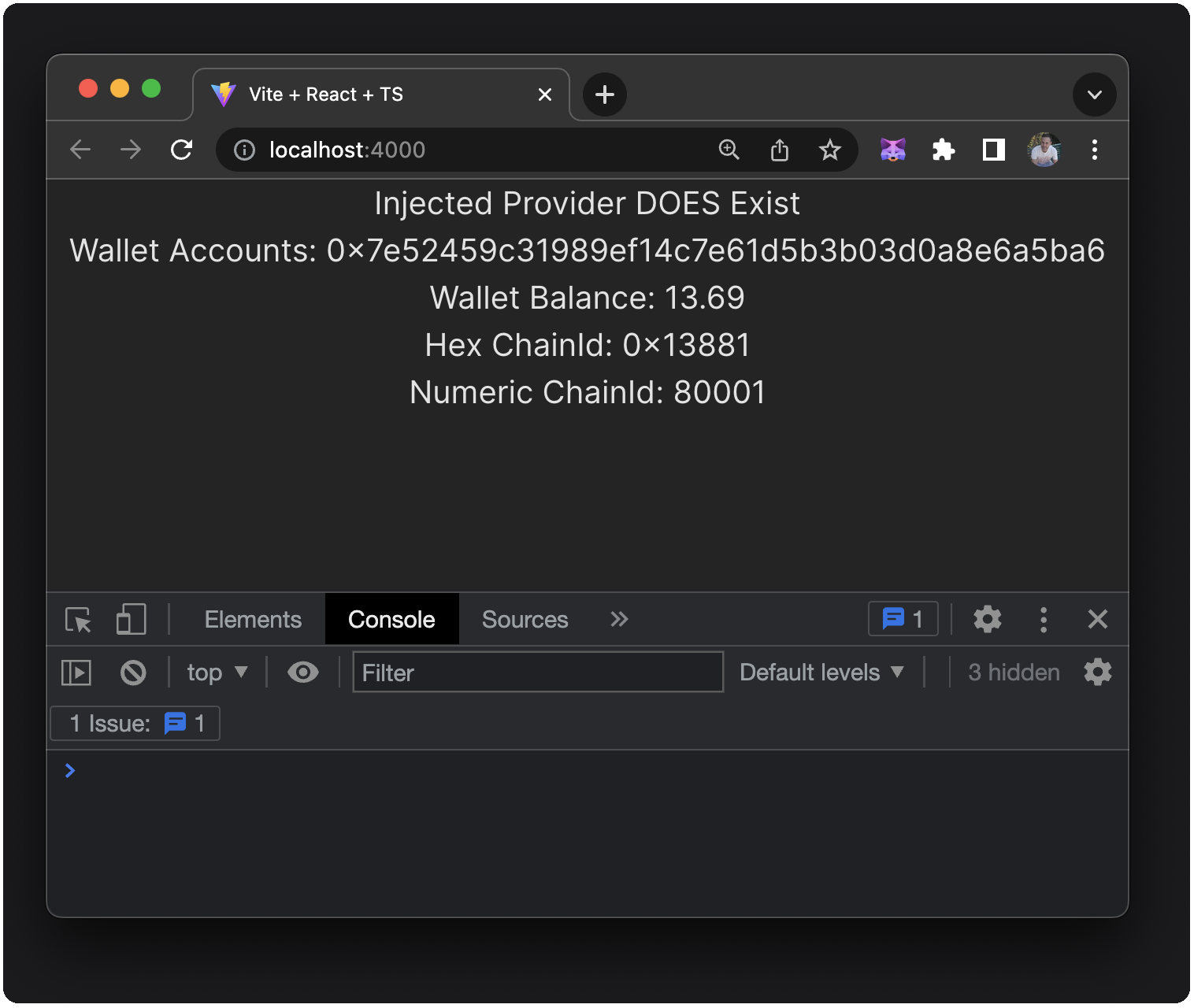
Your dapp detects any changes to balance or chainId. For the chainId, the utility functions convert the hex strings into a human-readable decimal value for display.
For chain IDs, you use the hex version in RPC calls and the decimal version for display.
To get the human-readable number of the chain, you use parseInt.
For this tutorial, your dapp only needs to display information about your wallet. For a real web3 dapp, you might add more functionality for switching chains programmatically or initiating transactions.
You might need to:
- Have a list of chain IDs that your dapp supports.
- Create UI that shows information on the supported networks.
- Present a button that allows users to connect to a supported network.
Detecting a user's network is crucial in almost every web3 dapp.
6. Handle errors
Now that you have a working dapp, you should set up error handling.
You can approach this in several ways; the following is a basic suggestion for handling an error or
rejection when the user connects their wallet using the handleConnect function.
You'll add useState to track isConnecting, error, and errorMessage.
When a user is in the middle of connecting, you'll disable the Connect MetaMask button.
If you receive an error, you'll update error to true and set the errorMessage for display.
You'll also set isConnecting back to false once either the user has connected or you've caught
the error, and set error back to false once the message is resolved.
Update src/App.tsx to the following:
import './App.css'
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import { formatBalance, formatChainAsNum } from './utils'
import detectEthereumProvider from '@metamask/detect-provider'
const App = () => {
const [hasProvider, setHasProvider] = useState<boolean | null>(null)
const initialState = { accounts: [], balance: "", chainId: "" }
const [wallet, setWallet] = useState(initialState)
const [isConnecting, setIsConnecting] = useState(false) /* New */
const [error, setError] = useState(false) /* New */
const [errorMessage, setErrorMessage] = useState("") /* New */
useEffect(() => {
const refreshAccounts = (accounts: any) => {
if (accounts.length > 0) {
updateWallet(accounts)
} else {
// if length 0, user is disconnected
setWallet(initialState)
}
}
const refreshChain = (chainId: any) => {
setWallet((wallet) => ({ ...wallet, chainId }))
}
const getProvider = async () => {
const provider = await detectEthereumProvider({ silent: true })
setHasProvider(Boolean(provider))
if (provider) {
const accounts = await window.ethereum.request(
{ method: 'eth_accounts' }
)
refreshAccounts(accounts)
window.ethereum.on('accountsChanged', refreshAccounts)
window.ethereum.on("chainChanged", refreshChain)
}
}
getProvider()
return () => {
window.ethereum?.removeListener('accountsChanged', refreshAccounts)
window.ethereum?.removeListener("chainChanged", refreshChain)
}
}, [])
const updateWallet = async (accounts: any) => {
const balance = formatBalance(await window.ethereum!.request({
method: "eth_getBalance",
params: [accounts[0], "latest"],
}))
const chainId = await window.ethereum!.request({
method: "eth_chainId",
})
setWallet({ accounts, balance, chainId })
}
const handleConnect = async () => { /* Updated */
setIsConnecting(true) /* New */
await window.ethereum.request({ /* Updated */
method: "eth_requestAccounts",
})
.then((accounts:[]) => { /* New */
setError(false) /* New */
updateWallet(accounts) /* New */
}) /* New */
.catch((err:any) => { /* New */
setError(true) /* New */
setErrorMessage(err.message) /* New */
}) /* New */
setIsConnecting(false) /* New */
}
const disableConnect = Boolean(wallet) && isConnecting
return (
<div className="App">
<div>Injected Provider {hasProvider ? 'DOES' : 'DOES NOT'} Exist</div>
{window.ethereum?.isMetaMask && wallet.accounts.length < 1 &&
/* Updated */
<button disabled={disableConnect} onClick={handleConnect}>Connect MetaMask</button>
}
{wallet.accounts.length > 0 &&
<>
<div>Wallet Accounts: {wallet.accounts[0]}</div>
<div>Wallet Balance: {wallet.balance}</div>
<div>Hex ChainId: {wallet.chainId}</div>
<div>Numeric ChainId: {formatChainAsNum(wallet.chainId)}</div>
</>
}
{ error && ( /* New code block */
<div onClick={() => setError(false)}>
<strong>Error:</strong> {errorMessage}
</div>
)
}
</div>
)
}
export default App
To test the error handling, disconnect from your accounts in MetaMask:
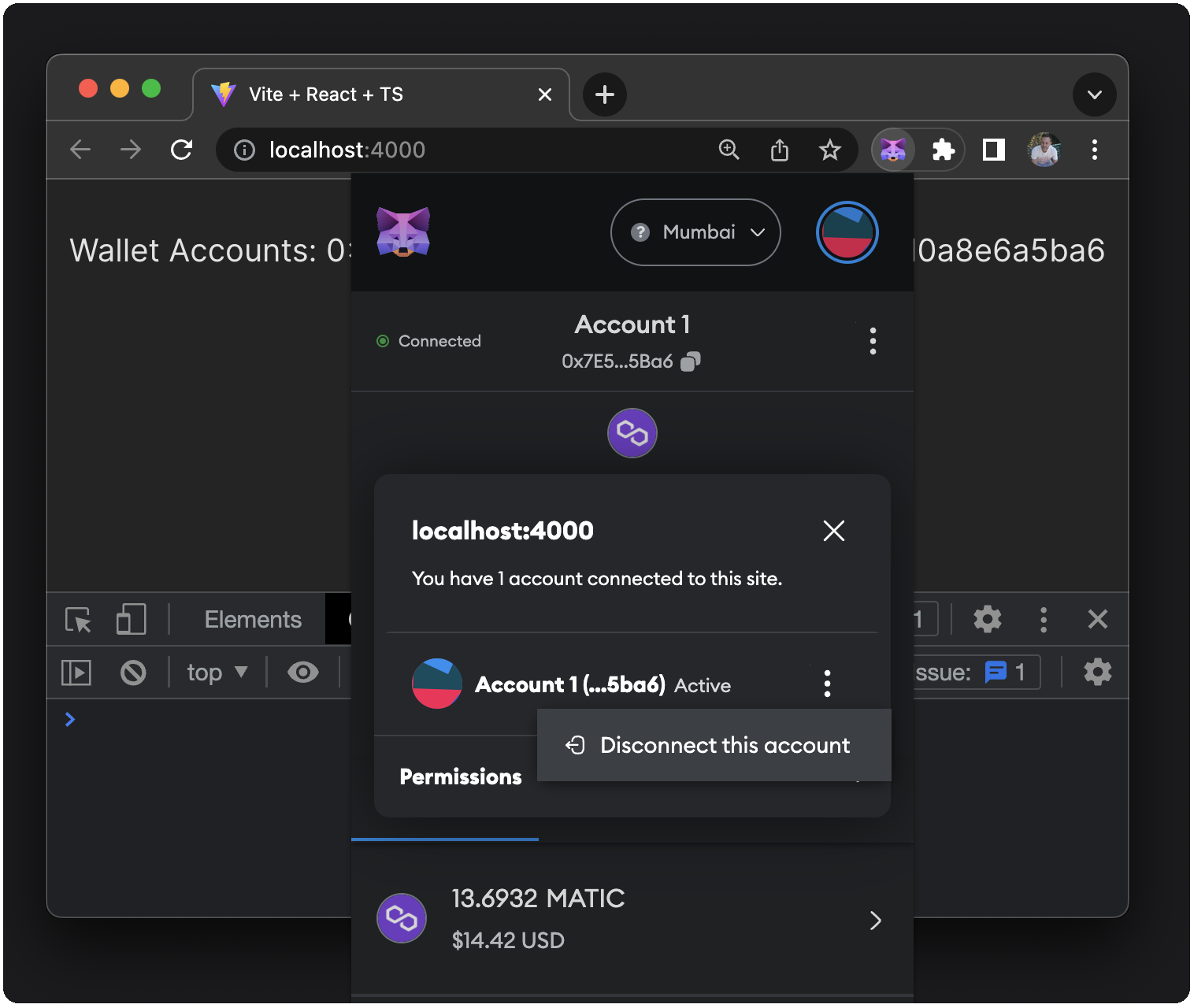
Attempt to connect again and choose to cancel the connection:
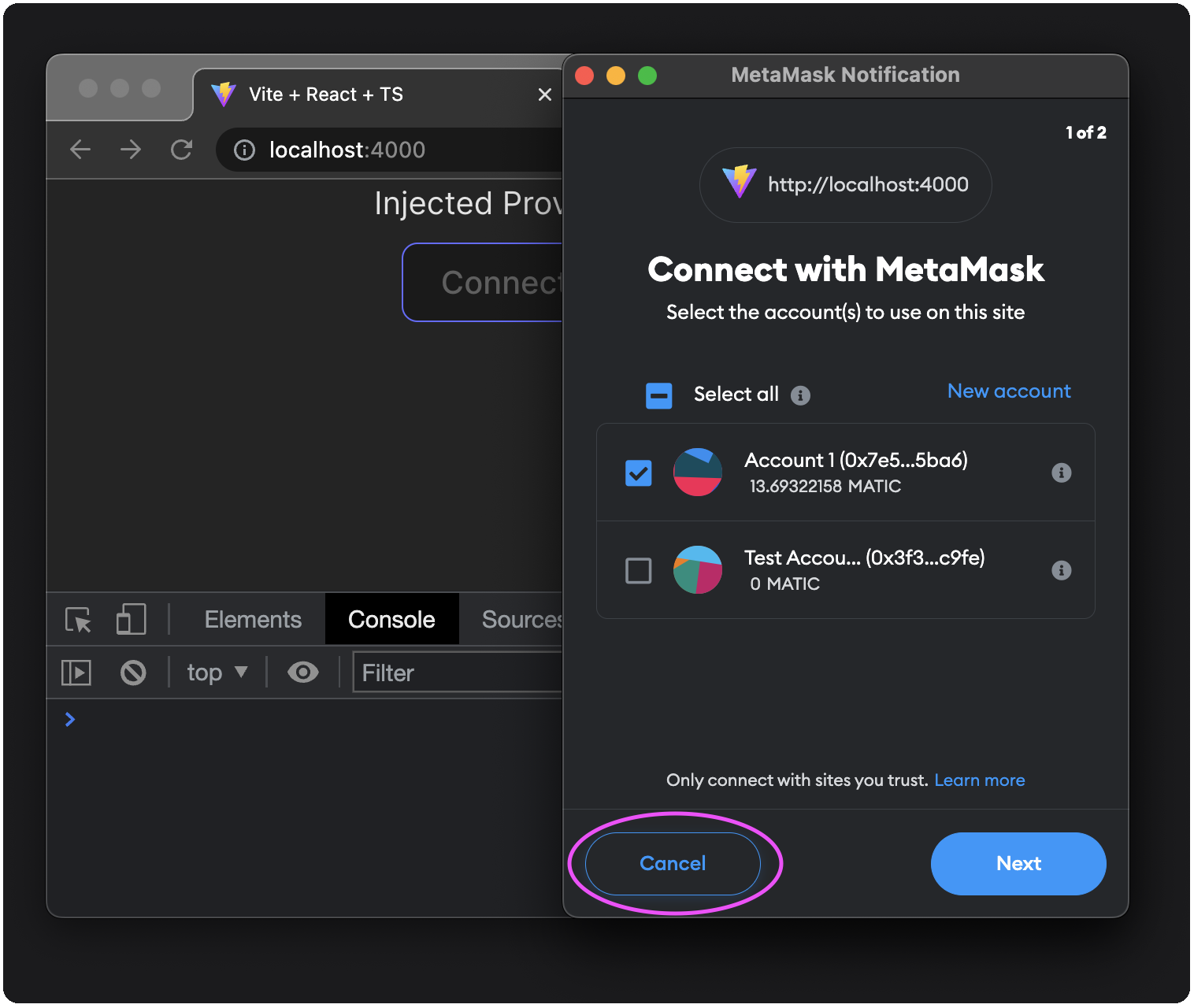
You'll see the error message displayed on the dapp and in the console:
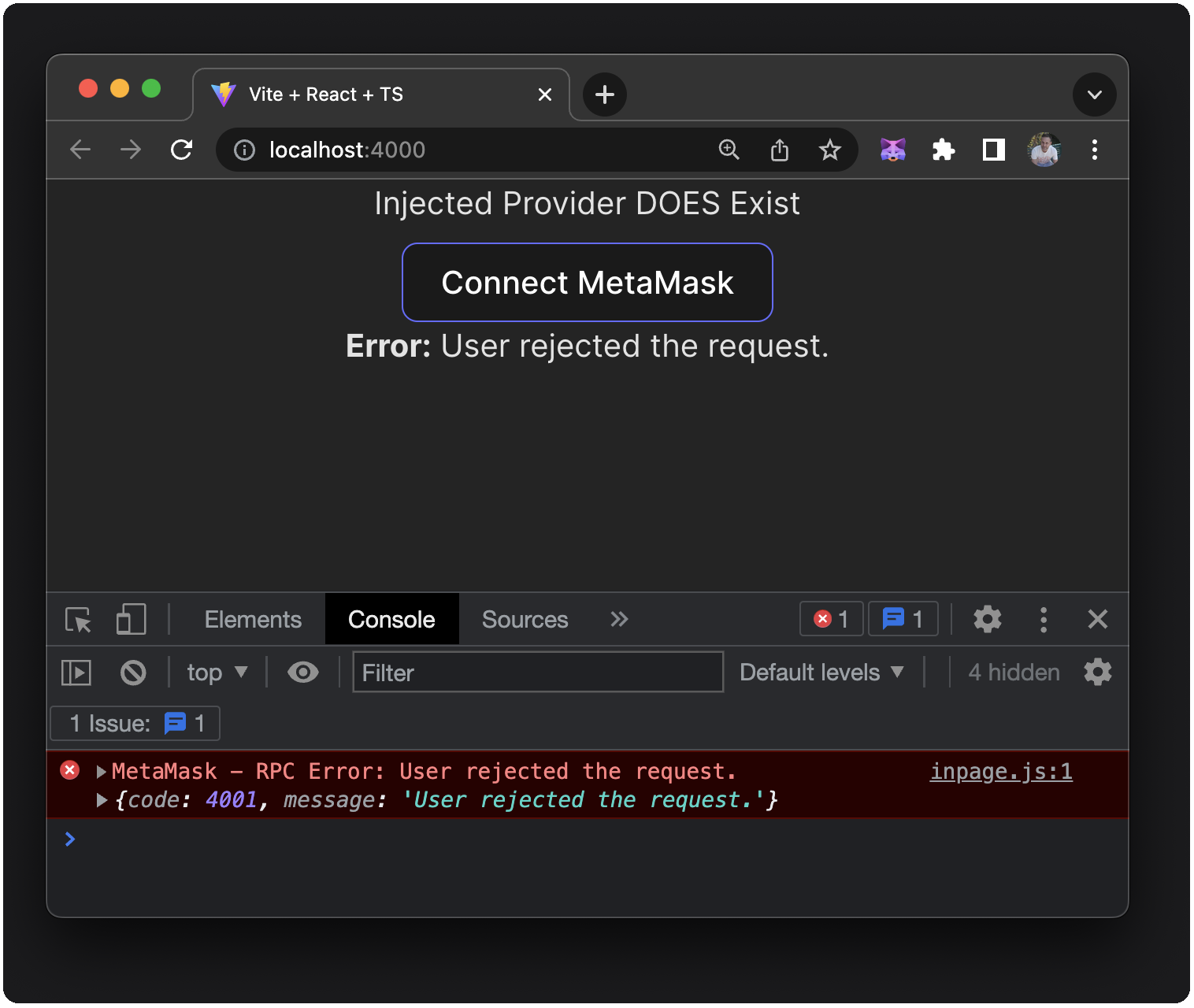
Conclusion
This tutorial walked you through creating a single component dapp using Vite, some basics of interacting with MetaMask and its API, and managing state locally.
You can see the source code for the final state of this dapp tutorial.
As a next step, you can create a React dapp with global state. This follow-up tutorial walks you through adding more than one component and working with global state. You'll use React's Context API to manage the state globally and ensure that any component in your dapp can be aware and conditionally render or display information about your MetaMask wallet.